[Top] [Prev] [Next] [Bottom]
This chapter uses an example to demonstrate how to configure the PortMaster to connect your office to another office using a dial-on-demand modem configuration. This type of connection is designed to take the place of a costly dedicated line between the two locations, where the amount and duration of traffic do not justify a leased line or Frame Relay connection.
This chapter also briefly describes how to configure multiline load balancing and ISDN BRI on-demand connections for office-to-office use.
The following topics are discussed:
The example described in this chapter connects a PortMaster Office Router located in a branch office in London with a PortMaster 2 in the headquarters in Paris. These models are used as an example; you can use any PortMaster for this configuration.
The PortMaster Office Router is designed to provide cost-effective connectivity between small remote (branch) offices and larger headquarters (main) offices. These types of connections are typically established on an as-needed basis. For most applications, a continuous connection is not cost-effective to maintain when a dial-on-demand connection can be established to transfer network traffic when necessary.
A dial-on-demand link establishes a connection with the specified location when network traffic is queued. The PortMaster PCMCIA Office Router OR-M is designed to support a dial-on-demand connection with another office using the PCMCIA modem port S1. Figure 15-1 shows an example of this configuration. The console port S0 can be used as a console, or with an external modem and a straight-through cable connected, as an additional dial on-demand port for multiline load balancing during peak traffic periods.
Office-to-Office Dial-On-Demand Configuration 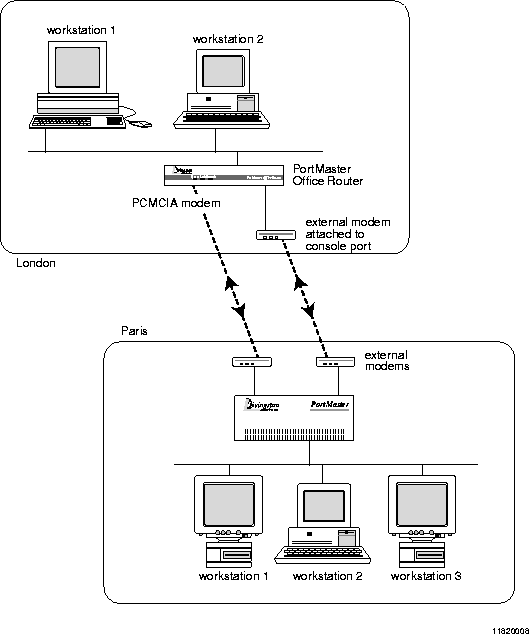
The PortMaster ISDN Office Router OR-U has an ISDN BRI port designated S1/S2 instead of a PCMCIA modem port. The ISDN port can be used for ISDN dial-on-demand connections.
The example in this chapter uses the PCMCIA asynchronous modem port on the OR-M. To use the ISDN port on the OR-U, see "Using ISDN for On-Demand Connections" on page 15-14.
The example described in this chapter connects a PortMaster router located in a branch office (London) with a PortMaster router located in the main office (Paris) using a dial--on-demand modem configuration.
To install your PortMaster, follow the instructions in your hardware installation guide. If you need additional help, refer to the troubleshooting chapter of the installation guide.
Once you have assigned an IP address to the PortMaster, continue with the steps. The following values shown in this chapter apply only to this example; when you are configuring your PortMaster, use values appropriate for your network.
-
Configure the following settings for the PortMaster PCMCIA Office Router in the London office:
a. Global settings (page 15-4).
b. Ethernet interface settings (page 15-4).
c. PCMCIA serial port settings (page 15-5).
d. Dial-in users (page 15-6).
e. Dial-out locations (page 15-7).
-
Configure the following settings for the PortMaster in the Paris office:
a. Ethernet interface settings (page 15-8).
b. Dial-out port settings (page 15-9).
c. Dial-in users (page 15-10).
d. Dial-out locations (page 15-11).
-
Test the configuration (page 15-12).
-
If necessary, configure the console port for multiline load balancing (page 15-13).
Alternatively, you can configure a PortMaster Office Router for ISDN dial-on-demand connections. See page 15-14 for instructions.
Configure the following settings on the PortMaster PCMCIA Office Router in the London office to enable London office users to access the main office network in Paris on demand.
Configure the global settings shown in Table 15-1. The values shown in the table only apply to this example. When you are configuring your PortMaster, use values appropriate for your network.
Once you have configured the global settings shown in Table 15-1, save the configuration by using the following command:
For more information about global settings, refer to Chapter 3, "Configuring Global Settings."
Configure the Ethernet settings shown in Table 15-2.
Once you have configured the Ethernet interface as shown in Table 15-2, save the configuration using the following command:
For more information on Ethernet settings, refer to Chapter 4, "Configuring the Ethernet Interface."
The PCMCIA modem port on the PortMaster Office Router is designated S1. Configure the port with the values shown in Table 15-3. You must install the PCMCIA modem to configure port S1.
Leave all the other settings at their default values. Once you have configured the port as shown in Table 15-3, reset the port and save the configuration using the following commands:
For more information about asynchronous ports, refer to Chapter 5, "Configuring an Asynchronous Port." For more information about configuring modems, refer to Chapter 10, "Using Modems."
You must set up a user account on the Office Router in the London office so the PortMaster 2 in the Paris office can dial in when traffic is queued at the main office. The new user paris should be configured with the values shown in Table 15-4.
Once you have configured the user table as shown in Table 15-4, save the configuration using the following command:
For more information about configuring user table settings, refer to Chapter 7, "Configuring Dial-In Users."
You must create a location entry on the PortMaster Office Router in the London office for the Paris office. This entry allows the Office Router in the London office to call the PortMaster 2 in the Paris office when network traffic is queued. The new location paris should be configured with the values shown in Table 17-5.
Note ¯  Configuring the maximum ports setting to a value higher than 0 causes the PortMaster to dial out to a continuous location, or become available for dial-out to an on-demand location. By configuring the maximum ports setting last, you ensure that the PortMaster will not attempt to make a connection with a location until you have configured all the settings for that location.
Configuring the maximum ports setting to a value higher than 0 causes the PortMaster to dial out to a continuous location, or become available for dial-out to an on-demand location. By configuring the maximum ports setting last, you ensure that the PortMaster will not attempt to make a connection with a location until you have configured all the settings for that location.
Once you have configured the location table as shown in Table 15-5, save the configuration using the following command:
For more information about configuring location table settings, refer to Chapter 8, "Configuring Dial-Out Connections."
In the example, the remote machine is a PortMaster 2 Communications Server in the Paris office.
Configure the Ethernet settings for the Paris office shown in Table 15-6.
Once you have configured the Ethernet interface as shown in Table 15-6, save the configuration using the following command:
For more information on Ethernet settings, refer to Chapter 4, "Configuring the Ethernet Interface."
For all ports on the PortMaster in Paris that you want enabled for dial-in and dial-out (two-way service) to the Office Router in the London office, enter the values shown in Table 15-7.
Leave all the other settings at their default values. Once you have configured the port as shown in Table 15-7, reset the port and save the configuration using the following commands:
For more information about asynchronous ports, refer to Chapter 5, "Configuring an Asynchronous Port."
A user account must be set up on the PortMaster in Paris so the Office Router in the London can dial in when traffic is queued. The new user london should be configured with the values shown in Table 15-8.
Once you have configured the user table as shown in Table 15-8, save the configuration using the following command:
For more information about configuring user table settings, refer to Chapter 7, "Configuring Dial-In Users."
You must create a location entry on the PortMaster in Paris for the London office. This entry allows the PortMaster in Paris to call the PortMaster in the London office when network traffic is queued. Configure a new location london with the values shown in Table 15-9.
Note ¯  Configuring the maximum ports setting to a value higher than 0 causes the PortMaster to dial out to a continuous location, or become available for dial-out to an on-demand location. By configuring the maximum ports setting last, you ensure that the PortMaster will not attempt to make a connection with a location until you have configured all the settings for that location.
Configuring the maximum ports setting to a value higher than 0 causes the PortMaster to dial out to a continuous location, or become available for dial-out to an on-demand location. By configuring the maximum ports setting last, you ensure that the PortMaster will not attempt to make a connection with a location until you have configured all the settings for that location.
Once you have configured the location table as shown in Table 15-9, save the configuration using the following command:
For more information about configuring location table settings, refer to Chapter 8, "Configuring Dial-Out Connections."
You should test the configuration before setting either of the locations for on-demand dialing. To test the configuration, follow these steps:
-
Enter the following commands to connect from the Paris office to the London office:
-
Monitor the dial-and-connect sequence between the two locations.
-
If everything connects as expected, reset the port on the Office Router in the Paris office, turn off debugging, and change the location type to on-demand:
-
If you notice a problem, do the following:
a. Reset the port on the Office Router in the Paris office.
b. Change the settings you think are causing the problem.
c. Dial the London office again.
d. Repeat this procedure until the connection is made correctly.
-
Repeat Steps 1 through 4, dialing from the London office to the Paris office.
Multiline load balancing is used to add additional lines when network traffic is heavy. If more than one line to the same location is established, the PortMaster balances the traffic among the lines. To configure the Office Router for multiline load balancing, you must attach an external modem to the console port.
In this example the console port is being configured for use as another serial port. Once you set this configuration, the port is no longer available for the system console. Figure 15-2 shows the multiline load balancing configuration.
Multiline Load Balancing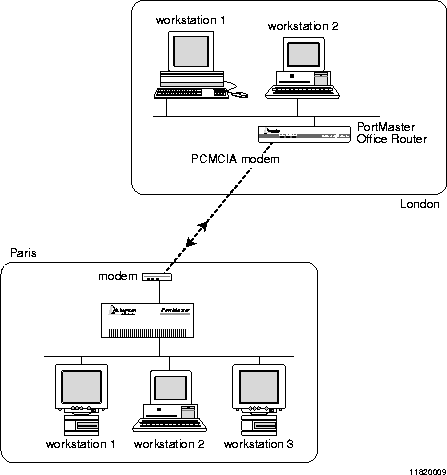
To enable multiline load balancing, you must configure the S0 port using the same settings shown for the PCMCIA port in Table 15-3. In addition, when you configure the location paris on the Office Router in the London office, use the values shown in Table 15-10 for the maximum number of ports and the high-water mark. See "Dial-Out Location Settings for London" on page 15-7 for the other values.
The value of the high-water mark depends on the type of traffic and how many bytes of traffic you want queued before the second line is used.
Using the ISDN BRI port on the PortMaster ISDN Office Router (OR-U) is very similar to using the PCMCIA port on the OR-M, except that you must do the following:
[Top] [Prev] [Next] [Bottom]
spider@livingston.com
Copyright © 1998, Livingston Enterprises, Inc. All rights
reserved.


